Wet Signatures vs. E-Signing: What You Need to Know
Table of contents
- What is a wet signature?
- Wet sign vs. e-sign: What's the difference?
- Types of signatures: Wet, electronic, and digital
- When should you use a wet signature?
- Advantages and disadvantages of wet signatures
- Will digital signatures replace handwritten ones?
- What if I want to replace wet signatures with digital ones?
-
About Concord
Effortless contract management, from drafting to e-signing and beyond. Book a live demo to see Concord in action.
Book a demo
Ever found yourself wondering whether to pick up a pen or click a button to sign a document? You’re not alone! Even in the digital age, old-fashioned wet signatures, where you physically put pen to paper, are still as legally binding as it gets.
In this article, we’ll dive into everything you need to know about wet signatures, how they stack up against electronic ones, and when to use each. So let’s get started!
What is a wet signature?
A wet signature is a traditional method of signing legal documents where an individual physically marks a paper document using ink. This is the signature most people are familiar with — a handwritten name or mark on a piece of paper that serves as proof of agreement or consent.
Wet sign vs. e-sign: What’s the difference?
Wet signatures and electronic signatures serve the same purpose but differ in their execution. While a wet signature involves a physical document, electronic signatures are used on electronic documents. The Electronic Signatures in Global and National Commerce Act (eSIGN Act) and the Uniform Electronic Transactions Act (UETA) in the United States, give electronic signatures the same legal standing as wet ink signatures in many scenarios.
Types of signatures: Wet, electronic, and digital
Today, signatures fall into three general categories.
- Wet signatures are physical pen-and-ink signatures on a paper document.
- Electronic signatures are signatures on electronic documents, often created by typing your name or signing a screen. There are several different types of electronic signatures to be aware of.
- Digital signatures are a subset of electronic signatures which come with an added layer of security involving encryption and signer authentication.
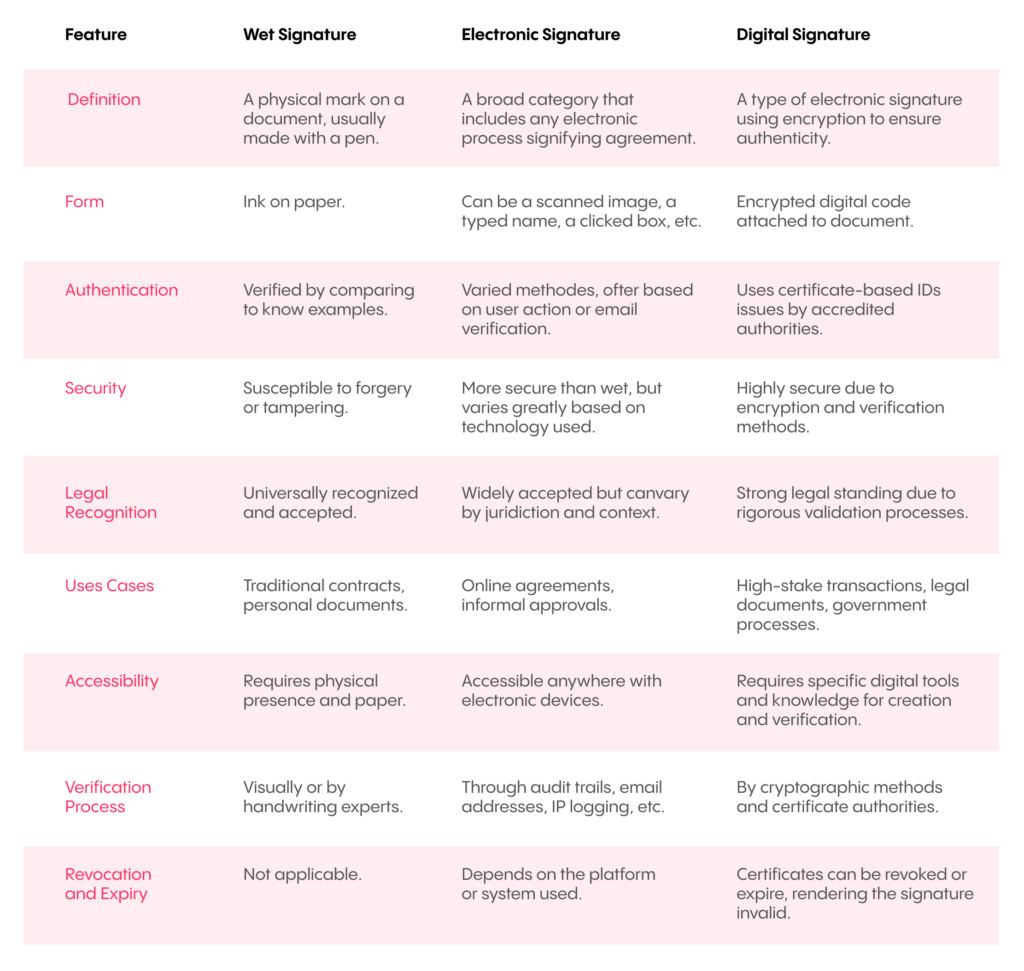
Each type of signature fits into different business processes in different ways. While many electronic signature formats are becoming more common, wet signatures are still mandatory in certain legal contexts.
When should you use a wet signature?
You should use a wet signature when legal requirements specifically mandate it. Wet signatures are still mandatory on the following types of documents:
- Legal affidavits: Sworn statements made under oath often require a wet signature to be considered valid.
- Notarized documents: Documents that require notarization, such as deeds or sworn statements, usually need to be signed in wet ink in the presence of a notary public.
- Certain types of real estate transactions: High-value transactions like buying or selling property often require wet signatures, especially for closing documents.
- Wills and testaments: These crucial legal documents usually require a wet signature to be considered legally binding.
- Power of attorney forms: Given the significant legal authority these documents confer, a wet signature is often required.
- Court orders: Legal orders issued by a judge typically need to be signed in wet ink to be enforceable.
- Marriage licenses: These legal documents often require a wet signature from both parties and sometimes witnesses.
- Adoption papers: Given the life-changing nature of adoption, these documents usually require a wet signature.
- Vehicle titles: When buying or selling a vehicle, the title often needs a wet signature for the transaction to be legally binding.
- Medical consent forms: In many jurisdictions, consent for medical procedures must be given via a document with a wet signature.
- Government tender documents: When bidding for a government contract, your tender document may require a wet signature.
- Intellectual property assignments: Transferring ownership of patents, copyrights, or other intellectual property often requires a wet signature.
- Immigration documents: Forms related to immigration and naturalization processes often require a wet signature.
- Financial loans and mortgages: Given the significant financial implications, these documents often require a wet signature for added security and legality.
If your document will be filed with a government agency that requires a wet signature, then you’ll need to sign in ink. In other cases, the receiving party may insist on a wet signature for their own internal processes. In all these cases, you’ll need to use a wet signature.
Advantages and disadvantages of wet signatures
Understanding the pros and cons of using wet signatures can help you make an informed decision on when to use this traditional form of signing. Here’s a deeper look into the advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages
- Universally accepted: Wet signatures have been around for centuries and are accepted globally. You’re unlikely to encounter a jurisdiction that doesn’t recognize them.
- Legally binding: In almost all legal systems, a wet ink signature on a document is considered a binding agreement, leaving little room for dispute.
- No technical infrastructure required: Unlike electronic or digital signatures, wet signatures don’t require any kind of technical setup, making them accessible to everyone, regardless of their comfort level with technology.
- Personal touch: A handwritten signature can add a personal element to documents, which can be important in certain contexts like handwritten letters or arts contracts.
Disadvantages
- Storage requirements: Physical documents with wet signatures need to be stored, often for long periods. This can consume a lot of space and require a system for easy retrieval.
- Slower process: Collecting wet signatures usually involves mailing documents or meeting in person, which can significantly slow down business processes.
- Risk of loss or damage: Physical documents are susceptible to risks like fire, water damage, or simple misplacement, which can result in the loss of important legal documents.
- Limited security: Unlike digital signatures, which often come with layers of encryption and authentication, wet signatures are easier to forge, and it’s harder to track who had access to the document.
By weighing these advantages and disadvantages in each signing situation, you can decide when a wet signature is the most appropriate method for your needs.
Will digital signatures replace handwritten ones?
Probably not. Although the trend is leaning toward electronic and digital signatures, it’s unlikely that wet signatures will ever be entirely phased out. Technological advances are making digital options more secure and accessible, but wet signatures are still the gold standard in many high-stakes legal situations, as outlined in the section above.
What if I want to replace wet signatures with digital ones?
If you’re considering making the switch to digital signing, just follow these steps:
- Assess signing requirements. Determine which of your organization’s documents can be digitally signed. The list in the section above may be a helpful guide.
- Understand the legal implications. Make sure you’re aware of the laws and regulations surrounding electronic and digital signatures in your jurisdiction.
- Choose the right signing platform. Some e-signature services only offer basic signing functionality, while contract management software platforms can also help you organize contracts, track deadlines, and automate approvals. When you consider how much time you spend getting digital contracts signed, and tracking them down in your internal filing system, an end-to-end contract management solution may be worth the investment.
Whether you’re a fan of the classic ink-on-paper method or you’re ready to jump into digital signing, it’s important to remember that there’s a time and place for both. Electronic and digital signatures are convenient and quick, but let’s not forget that wet signatures still have their special moments, especially when the law steps in. In both cases, you’re now equipped with the know-how to tackle any signing situation that comes your way.



